See also Bibiana’s Google Scholar profile for an account of her publications only.
ORCID:0000-0002-6715-7294.
Names in bold denote group members; underlined names correspond to supervised PhD and MSc students; asterisks (*) indicate undergraduate students, interns and mentees.
Under review/In revision
70. White TE‡ , Rojas B‡, Mappes J & Kemp D. Seeing through the light: colour contrasts dominate human detection of coloured stimuli in natural scenes. (‡Equal contribution)
2026
69. Rojas B, Rojas-Montoya M*‡ & Carvajal-Castro JD‡ Beyond protection from predators: correlates and additional benefits of aposematic signalling. (‡Equal contribution). Accepted for publication. Advances in the Study of Behaviour.
68. Nemesházi E, Ujhegyi N, Mikó Z, Kásler A, Lente V, et al. Photo-based individual identification is more reliable than visible implant elastomer tags or toe-tipping in young agile frogs. PLOS ONE 21: e0342340. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0342340
67. Rojas B, Rueda-Solano LA & Vargas-Salinas F. Natural history in the backyard: a comment on Guevara-Fiore 2025. Behavioral Ecology arag008. DOI:10.1093/beheco/arag008

66. Nemesházi E, Mikó Z, Ujhegyi N, Kásler A, Lehofer N, et al. Placing anurans in water can improve photo-based individual identification. PLOS ONE 21: e0341460. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0341460
65. Schlippe Justicia L, Dittrich C, Nokelainen O & Rojas B. Defensive colouration is not a reliable indicator of fungal infection in aposematic poison frogs. Behavioral Ecology araf137. DOI: 10.1093/beheco/araf137.
2025
64. Schlippe Justicia L, Pašukonis A & Rojas, B. Phytotelmata. Quick Guide. Current Biology 35, R1127–R1141.
63. Burdfield-Steel E, Ottocento C, Furlanetto M, Rojas B, Nokelainen O & Mappes J. Honest signalling in predator-prey interactions: testing the resource allocation hypothesis. Functional Ecology 39: 2833-2848. DOI: 10.1111/1365-2435.70122
62. Nemesházi, E. & Bókony, V. 2025 Interplay of genotypic and thermal effects on sex determination shapes climatic distribution in herpetofauna. Global Ecology and Biogeography 34: e70096. DOI:10.1111/geb.70096.
61. Hagnier D‡, Dittrich C‡, Van den Bos M* & Rojas B. Habitat alteration impacts predation risk in an aposematic amphibian. (‡Equal contribution). Journal of Zoology 327:60-72. (doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/jzo.70036).
60. Mikó Z, Bókony V, Ujhegyi N, Nemesházi E, Erös R, Orf S, Hettyey A. 2025. Weak effects of chlorpyrifos at environmentally relevant concentrations on fitness-related traits in agile frogs. Aquatic Toxicology 284:107400. DOI:10.1016/j.aquatox.2025.107400.
59. Galarza JA, Nokelainen O, Brien ML, Rojas B, Valkonen J, Chunashvili T, Tasane T & Mappes J. Genetic and phenotypic variation in wood tiger moths from the Caucasus: insights into male warning colour variation. Insect Science 10.1111/1744-7917.70101. DOI:10.1111/1744-7917.70101.
58. Dittrich, C.‡, Mangione, R.‡, Marquis, O., Ringler, E. and Lemaire, J. Ecological and behavioral implications of multiple paternity in the smooth-fronted caiman in French Guiana. Ecology & Evolution 15: e71337. DOI:10.1002/ece3.71337 (‡Equal contribution)
57. Penacchio O, Hämäläinen L, Rojas B, Summers K, Yeager J, Sherratt T & Exnerová A. Cognitive ecology of surprise in predator-prey interactions. Functional Ecology 39: 664-680. DOI: 10.1111/1365-2435.14750. PDF
56. Mayer M, Schlippe Justicia L & Rojas B. Phenotypic divergence across populations does not affect habitat selection in an Amazonian poison frog. Global Ecology and Conservation 75, e03358. DOI:10.1016/j.gecco.2024.e03358 PDF
2024
55. Kosch, T.A., Torres-Sánchez, M., Liedtke, H.C., Summers, K., Yun, M.H., Crawford, A.J., Maddock, S.T., Ahammed, M.S., Araújo, V.L.N., Bertola, L.V… Dittrich, C.… et al. 2024. The Amphibian Genomics Consortium: advancing genomic and genetic resources for amphibian research and conservation. BMC Genomics 25, 1025. DOI: 10.1186/s12864-024-10899-7
54. Desvars-Larrive A, Burger P, Khol JL, Posautz A, Schernhammer E, Kutalek R, Puspitarani GA, Schlippe Justicia L, Springer DN, Ernst D, Sohm C, Pontel de Almeida A, Schobesberger H, Knauf S & Walzer C. 2024 Launching Austria’s One Health network: paving the way for transdisciplinary collaborations. One Health Outlook 6, 23. DOI: 10.1186/s42522-024-00116-6.
 53. Rojas B & Vargas-Salinas F. Developments in the study of poison frog evolutionary ecology II: decoding hidden messages in their coloration and unique behaviours. Evolutionary Ecology DOI: 10.1007/s10682-024-10316-1
53. Rojas B & Vargas-Salinas F. Developments in the study of poison frog evolutionary ecology II: decoding hidden messages in their coloration and unique behaviours. Evolutionary Ecology DOI: 10.1007/s10682-024-10316-1
*Journal cover: Different species of poison frogs (sensu lato): Dendrobates truncatus (top left), Atelopus zeteki (bottom left), Mantella sp (centre), Melanophryniscus rubriventris (top right), Hyloxalus awa (bottom right). Illustrations: Lia Schlippe Justicia.
52. Dittrich C‡, Hölzl F‡, Smith S, Fouilloux C, Parker DJ, O’Connell LA, Knowles LS, Hughes M, Fewings A, Morgan R, Rojas B, & Comeault A. Genome assembly of the dyeing poison frog provides insights into the dynamics of transposable element and genome-size evolution. Genome Biology and Evolution 16: evae109 DOI: 10.1093/gbe/evae109 (‡Equal contribution)
51. Vargas-Salinas F & Rojas B. 2024. Developments in the study of poison frog evolutionary ecology I: social interactions, life history and space use across space and ontogeny. Evolutionary Ecology 38:1-22. DOI: 10.1007/s10682-024-10296-2 PDF
50. Rojas B, Dittrich C & Calhim, S. 2024. Testes size seen through the glass of amphibian care. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 39: 421-423. DOI: 10.1016/j.tree.2024.04.001 PDF
49. Schlippe Justicia L, Lemaire J, Dittrich C, Mayer M, Bustamante P & Rojas B. 2024. Poison in the nursery: mercury contamination in the tadpole-rearing sites of an Amazonian frog. Science of the Total Environment 912:169450 DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.169450 PDF
48. Ottocento C‡, Rojas B‡, Burdfield-Steel E, Furlanetto M, Nokelainen O & Mappes J. 2024. Diet influences resource allocation in chemical defence but not melanin synthesis in an aposematic moth. ‡Shared first authorship. Journal of Experimental Biology 227: jeb245946. DOI:10.1242/jeb.245946 PDF
 47. Schlippe Justicia L, Mayer M, Lorioux-Chevalier U, Dittrich C, Rojas B & Chouteau M. 2024. Intraspecific divergence in sexual size dimorphism and reproductive strategies in a polytypic poison frog. Evolutionary Ecology 38: 121–139. DOI: 10.1007/s10682-023-10280-2 PDF
47. Schlippe Justicia L, Mayer M, Lorioux-Chevalier U, Dittrich C, Rojas B & Chouteau M. 2024. Intraspecific divergence in sexual size dimorphism and reproductive strategies in a polytypic poison frog. Evolutionary Ecology 38: 121–139. DOI: 10.1007/s10682-023-10280-2 PDF
*Journal cover: Different morphs of Dendrobates tinctorius across French Guiana. Illustrations: Lia Schlippe Justicia
2023
46. Ringler E, Rojas B, Stynoski J & Schulte LM. 2023. What amphibians can teach us about the evolution of parental care. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution and Systematics 54:43–62 DOI:10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-102221-050519 PDF
45. Rojas B, Lawrence JP & Márquez R. 2023. Amphibian Coloration: Proximate Mechanisms, Function, and Evolution. Pp. 219-258. In: G. Rueda-Moreno and M. Comas (Eds). Evolutionary Ecology of Amphibians. CRC Press. PDF
44. Kikuchi, D.W., Allen, W.L., Arbuckle, K., Aubier, T.G., Briolat, E.S., Burdfield-Steel, E.R., Cheney, K.L., Daňková, K., Elias, M., Hämäläinen, L., Herberstein, M.E., Hossie, T.J., Joron, M., Kunte, K., Leavell, B.C., Lindstedt, C., Lorioux Chevalier, U., McClure, M., McLellan, C.F., Medina, I., Nawge, V., Páez, E., Pal, A., Pekár, S., Penacchio, O., Raška, J., Reader, T., Rojas B., Rönkä, K.H., Rößler, D.C., Rowe, C. Rowland, H.M., Roy, A., Schaal, K.A., Sherratt, T.N., Skelhorn, J., Smart, H.R., Stankowich, T., Stefan, A.M., Summers, K., Taylor, C.H., Thorogood, R., Umbers, K., Winters, A.E., Yeager, J. & Exnerová, A. The evolution and ecology of multiple antipredator defences. Journal of Evolutionary Biology 36: 975–991. DOI: 10.1111/jeb.14192
43. Hernández T*, Rueda LA, Valkonen J & Rojas B. 2023. Predator response to the coloured eyespots and defensive posture of Colombian four-eyed frogs. Journal of Evolutionary Biology 36: 1040–1049. DOI: 0.1111/jeb.14193
42. Fouilloux C, Yovanovich C, Stynoski J & Rojas B. 2023. Visual environment of rearing sites affects larval response to perceived risk in poison frogs. Journal of Experimental Biology 226: jeb245822 DOI:10.1242/jeb.245822
41. Lawrence JP, Rojas B, Blanchette A, Saporito R, Mappes J, Fouquet A & Noonan BP. 2023. Linking predator responses to alkaloid variability in poison frogs. Journal of Chemical Ecology 49: 195–204. DOI:10.1007/s10886-023-01412-7
40. Ottocento C, Winters A, Rojas B, Mappes J & Burdfield-Steel E. 2023. Not just the sum of its parts: geographic variation and non-additive effects of pyrazines in the chemical defence of an aposematic moth. Journal of Evolutionary Biology 36:1020-1031. DOI: 10.1111/jeb.14142
39. Schlippe-Justicia L, Fouilloux C & Rojas B. 2023. Poison frog social behaviour under global change: potential impacts and future challenges. Acta Ethologica 26: 151–166– Special Issue: “Impact of global change on social interactions: ecological and fitness implications”.DOI: 10.1007/s10211-022-00400-6 PDF
2022
38. Pašukonis A, Serrano-Rojas SJ, Fischer MT, Loretto MC, Shaykevich DA, Rojas B, Max Ringler M, Roland A-B, Marcillo-Lara A, Ringler E, Rodríguez C, Coloma LA, O’Connell LA. 2022. Contrasting parental roles shape sex differences in poison frog space use but not navigational performance. eLife 11:e80483. DOI:10.7554/eLife.80483
37. Fouilloux C, Fromhage L, Valkonen J & Rojas B. 2022.Size-dependent aggression towards kin in a cannibalistic species. Behavioral Ecology 33:582–591. DOI: 10.1093/beheco/arac020
Featured in: Phys.org, IFLScience!, Science Daily, Discover Magazine

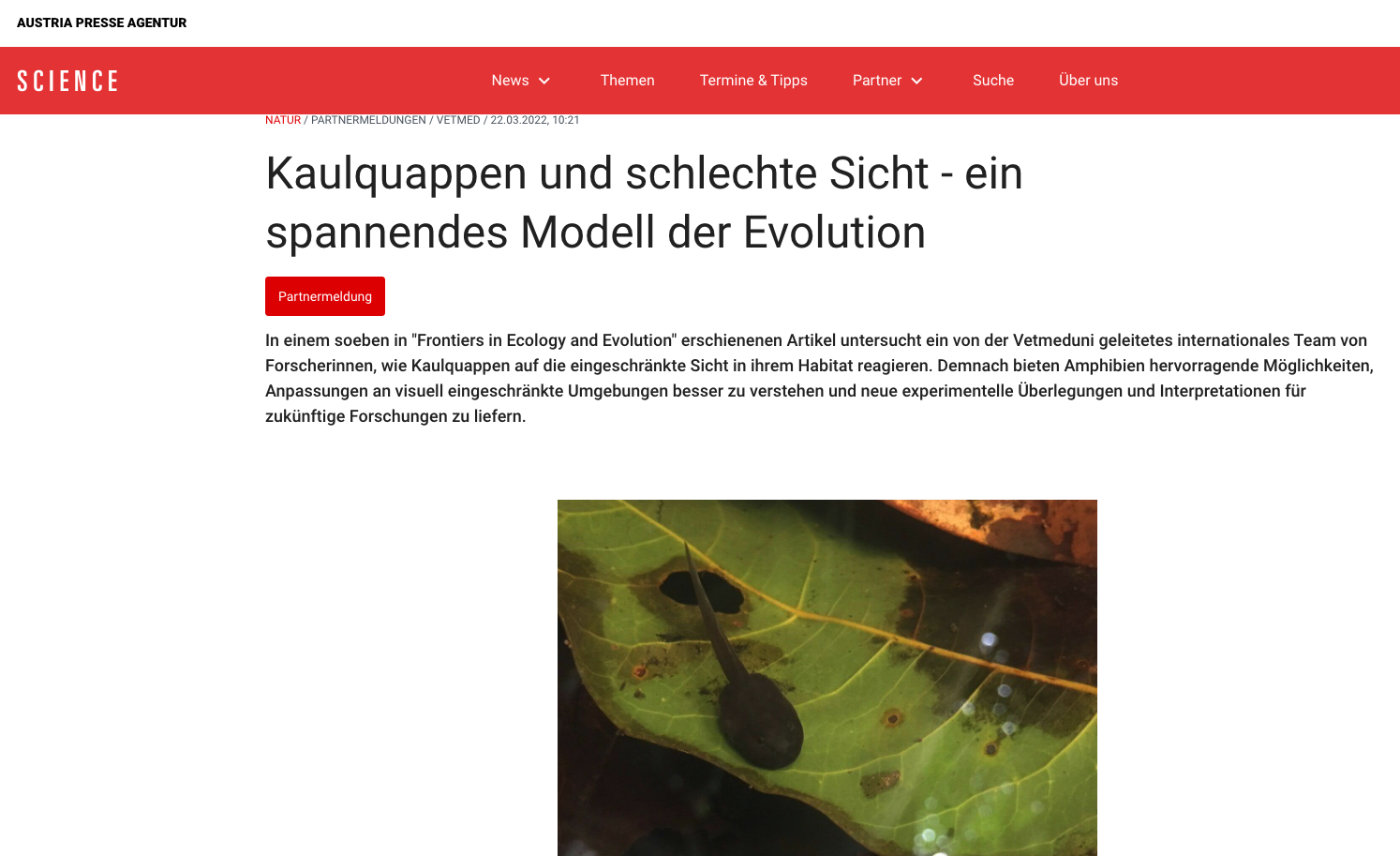
36. Fouilloux C, Yovanovich C, Rojas B. Tadpole responses to environments with limited visibility: what we (don’t) know and perspectives for a sharper future. Frontiers in Ecology & Evolution 9:766725. DOI: 10.3389/fevo.2021.766725
Featured in: APA Science
2021
35. Carvajal-Castro, J. D.*, Vargas-Salinas, F., Casas-Cardona, S., Rojas, B. & Santos, J.C. Aposematism facilitates the diversification of parental care strategies in poison frogs. Scientific Reports 11:19047. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-97206-6
34. Fouilloux, C., Serrano Rojas, S. J.*, Carvajal-Castro, J. D.*, Valkonen, J., Gaucher, P., Fischer, M.-T., Pašukonis, A.‡ & Rojas, B.‡ 2021. Pool choice in a vertical landscape: tadpole rearing site flexibility in phytotelm-breeding frogs. Ecology & Evolution 11: 9021– 9038. DOI:10.1002/ece3.7741 (‡ Equal contribution as senior authors). PDF
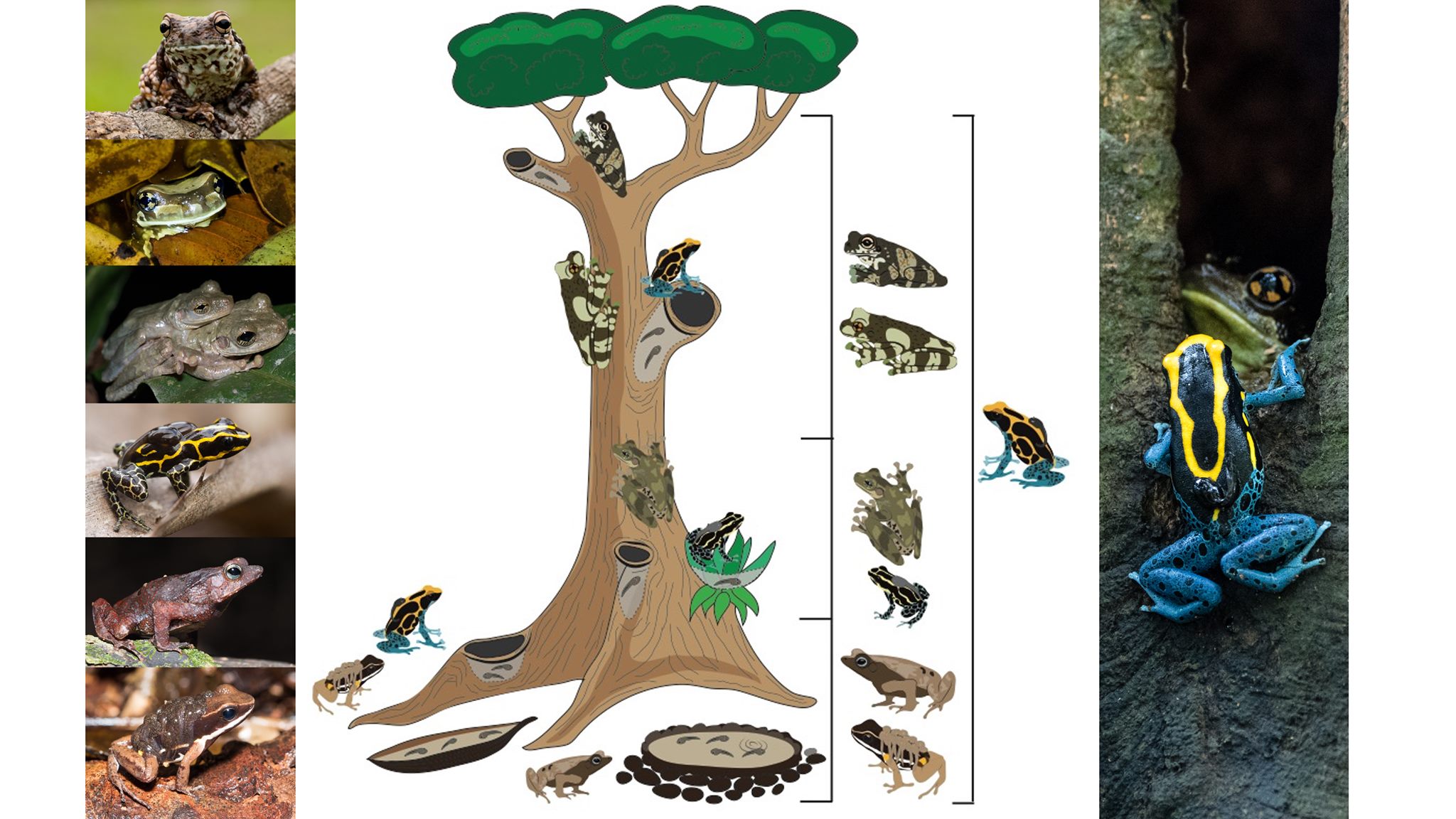
Featured in: Science Daily, YLE News, Phys.org

2020
33. Rönkä, K., Valkonen, J., Nokelainen, O., Rojas, B., Gordon, S., Burdfield-Steel, E. & Mappes, J. Geographic mosaic of selection by avian predators on hindwing warning colour of a polymorphic aposematic moth. Ecology Letters 23:1654-1663.DOI: 10.1111/ele.13597 PDF
32. Fouilloux, C,. Garcia-Costoya, G. & Rojas, B. Visible implant elastomer (VIE) success in early larval stages of a tropical amphibian species. PeerJ 8:e9630 DOI: 10.7717/peerj.9630

31. Schulte, L. M., Ringler, E.‡, Rojas, B.‡ & Stynoski, J. L.‡ 2020. Developments in amphibian parental care research: history, present advances and future perspectives. (‡Equal contribution; listed in alphabetical order). Herpetological Monographs 34:71-97. DOI: 10.1655/HERPMONOGRAPHS-D-19-00002.1 PDF
Featured in: AmphibiaWeb on September 21, 2020
*Journal cover: A female Cryptobatrachus boulengeri from the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta, Colombia. Photo: L.A. Rueda©
30. Carvajal-Castro, J. D.*, López-Aguirre, Y., Ospina, A. M., Santos, J. C., Rojas, B. & Vargas-Salinas, F. 2020. Much more than a clasp: evolutionary patterns of amplexus diversity in anurans. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society 129:652-663. DOI: 10.1093/biolinnean/blaa009
2019
29. Fouilloux, C., Ringler, E. & Rojas, B. 2019. Cannibalism. Quick Guide. Current Biology 29:R1295-R1297. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.09.068
28. Rojas, B.& Pašukonis, A. 2019. From habitat use to social behavior: natural history of a voiceless poison frog, Dendrobates tinctorius. PeerJ 7:e7648. DOI: 10.7717/peerj.7648PDF
27. Lawrence, J. P.‡,Rojas, B.‡, Fouquet, A., Mappes, J., Blanchette , A., Saporito, R., Bosque, R. J., Courtois, E., & Noonan, B. P. 2019. Weak warning signals can persist in the absence of gene flow. (‡Equal contribution). PNAS 116:19037-19045. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1901872116. PDF
Featured in: The New York Times, Science Daly, Phys.org, Dr.Stevil’s Blog, Cosmos Magazine, ELEMENT (Russia), GreenReport (Italy).

26. Pašukonis, A., Loretto, M. C. & Rojas, B. 2019. How far do tadpoles travel in the rainforest? Parent-assisted dispersal in poison frogs. Evolutionary Ecology 33: 613-623. DOI:10.1007/s10682-019-09994-z PDF
Featured in: Scientific American, GreenReport (Italy), Dr. Stevil’s Youtube Channel.

25. Rojas, B., Mappes, J. & Burdfield-Steel, E. 2019. Multiple modalities in insect warning displays have additive effects against wild avian predators. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 73:37. DOI: 10.1007/s00265-019-2643-6 PDF
24. Bernal, X. E., Rojas, B., Pinto-E, M. A., Mendoza-Henao, Á. M., Herrera-Montes, A., Herrera-Montes, M. I. and Cáceres Franco, A. P. 2019. Empowering Latina scientists. Science 363:825. DOI: 10.1126/science.aaw600 PDF
2018
23. Burdfield-Steel, E., Brain, M., Rojas, B. & Mappes, J. 2018. The price of safety: food deprivation in early life influences the efficacy of chemical defence in an aposematic moth. Oikos 128:245-253. DOI:10.1111/oik.05420
22. Rojas, B., Burdfield-Steel, E., Gordon, S. P., De Pasqual, C., Hernández, L.*, Mappes, J., Nokelainen, O., Rönkä, K., Lindstedt, C. 2018. Multimodal aposematic signals and their emerging role in mate attraction. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution 9:93. DOI: 10.3389/fevo.2018.00093
21. Rönkä, K., Mappes, J., Kiviö, R., Salokannas, J., Michalis, C. & Rojas, B. 2018. Can multiple-model mimicry explain warning signal polymorphism in the wood tiger moth, Arctia plantaginis (Lepidoptera: Erebidae)? Biological Journal of the Linnean Society 124: 237-260. DOI: 10.1093/biolinnean/bly042 PDF
20. Burdfield-Steel, E., Pakkanen, H., Rojas, B., Galarza, J. A. & Mappes, J. 2018. De novo synthesis of chemical defences in an aposematic moth. Journal of Insect Science 18(2):28. DOI:10.1093/jisesa/iey020 PDF
19. Henze, M. J., Lind, O., Mappes, J., Rojas, B. and Kelber, A. 2018. An aposematic colour‐polymorphic moth seen through the eyes of conspecifics and predators ‐ sensitivity and colour discrimination in a tiger moth. Functional Ecology 32: 1797-1809. DOI:10.1111/1365-2435.13100 PDF
18. Rönkä, K., De Pasqual, C., Mappes, J., Gordon, S. P. & Rojas, B. 2018. Colour alone matters: no predator generalisation among morphs of an aposematic moth. Animal Behaviour 135: 153–163. DOI: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2017.11.015 PDF
2017
17. Rojas, B.‡, Burdfield-Steel, E.‡, Pakkanen, H., Suisto, K., Maczka, M., Schulz, S. & Mappes, J. 2017. How to fight multiple enemies: target-specific chemical defences in an aposematic moth. (‡Equal contribution). Proceedings of the Royal Society B 284: 20171424. DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2017.1424 PDF
Featured in: Inside Science, DiscoverMagazine, Scientific American’s “60 Second Science” podcast, Phys.org, Science Daily.

16. White, T. E., Rojas, B., Mappes, J., Rautiala, P. & Kemp, D. J. 2017. Colour and luminance contrasts predict the human detection of natural stimuli in complex visual environments. Biology Letters 13: 20170375. DOI: 10.1098/rsbl.2017.0375 PDF
15. Rojas, B. 2017. Behavioural, ecological, and evolutionary aspects of diversity in frog colour patterns. Biological Reviews 92:1059-1080. DOI: 10.1111/brv.12269 PDF
2015
14. Stynoski, J. L.‡, Schulte, L. M.‡ & Rojas, B.‡ 2015. Poison frogs. Quick Guide. Current Biology 25:R1026–R1028.(‡ Equal contribution) DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.06.044 PDF
13. Rojas, B. 2015. Mind the gap: treefalls as drivers of parental tradeoffs. Ecology & Evolution 5:4028-4036. DOI: 10.1002/ece3.1648 PDF
Featured in: Sciences et Avenir (France)
12. Rojas, B.‡, Gordon, S. P.‡ & Mappes, J. 2015. Frequency-dependent flight activity in the colour polymorphic wood tiger moth. Current Zoology 61:765-772. Special issue on ‘Anti-predator coloration and behavior’ (‡ Equal contribution) DOI: 10.1093/czoolo/61.4.765 PDF
11. Gordon, S. P., Kokko, H., Rojas, B., Nokelainen, O. & Mappes, J. 2015. Colour polymorphism torn apart by opposing positive frequency-dependent selection, yet maintained in space. Journal of Animal Ecology 84:1555-1564. DOI: 10.1111/1365-2656.12416 PDF
Featured in a Special Virtual Issue on Evolutionary Ecology (editor’s choice) in the Journal of Animal Ecology
10. Exnerová, A., Jezová, D., Štys, P., Doktorovová, L., Rojas, B. & Mappes, J. 2015. Different reactions to aposematic prey in 2 geographically distant populations of great tits. Behavioral Ecology 26:1361-1370. DOI: 10.1093/beheco/arv086 PDF
9. Hämäläinen, L., Valkonen, J., Mappes, J. & Rojas, B. 2015. Visual illusions in predator-prey interactions: birds find moving patterned prey harder to catch. Animal Cognition 18:1059-1068. DOI: 10.1007/s10071-015-0874-0 PDF
8. Rojas, B., Valkonen, J. & Nokelainen, O. 2015. Aposematism. Quick Guide. Current Biology 25:R350-R351. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.02.015 PDF
2014
7. Rojas, B., Rautiala, P. & Mappes, J. 2014. Differential detectability of polymorphic warning signals under varying light environments. Behavioural Processes 109(B): 164-172. Special issue on ‘Animal Cognition in the Wild’. DOI: 10.1016/j.beproc.2014.08.014 PDF
6. Rojas, B., Devillechabrolle, J. & Endler, J. A. 2014. Paradox lost: variable colour-pattern geometry is associated with differences in movement in aposematic frogs. Biology Letters 10: 20140193. DOI: 10.1098/rsbl.2014.0193 PDF
*Journal cover: A male Dendrobates tinctorius from Nouragues Natural Reserve, French Guiana. Photo: Bibiana Rojas
Featured in: Phys.org, Science News, Daily Mail (UK), Sydney Morning Herald (Australia), Nature World News, Spektrum (Germany), France Inter.
5. Rojas, B. 2014. Strange parental decisions: fathers of the dyeing poison frog deposit their tadpoles in pools occupied by large cannibals. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 68:551-559. DOI: 10.1007/s00265-013-1670-y PDF
Featured in: Science Magazine, Science Daily, Phys.org, Springer Select, The Scientist magazine, Der Standard (Austria), Scinexx (Germany).

2013
4. Rojas, B. & Endler, J. A. 2013. Sexual dimorphism and intra-populational colour pattern variation in the aposematic frog Dendrobates tinctorius. Special Issue on the ‘Evolutionary Ecology of Poison Frogs’. Evolutionary Ecology 27:739-753. DOI: 10.1007/s10682-013-9640-4 PDF
2012
3. Ringler, E., Rojas, B., Ringler, M. & Hödl, W. 2012. Characterisation of nine polymorphic microsatellite loci in the dyeing poison frog Dendrobates tinctorius (Dendrobatidae), and their cross-species utility in two other dendrobatoid species. Herpetological Journal 22: 265-267. PDF
Before 2012
2. Endler, J. A. & Rojas, B. 2009. The spatial pattern of natural selection when selection depends on experience. American Naturalist 173: E62-E78. DOI: 10.1086/596528 PDF
1. Rojas, B., Amézquita, A. & Delgadillo, A. 2006. Matching and symmetry in the frequency recognition curve of the poison frog Epipedobates trivittatus. Ethology 112: 564-571. DOI: 10.1111/j.1439-0310.2005.01190.x PDF
In the pipeline
Schlippe Justicia L, Ferreira S, Hoelzl F, Dittrich C, Mayer M & Rojas B. The interactive effects of habitat disturbance and Bd infection patterns on the skin bacterial communities in a Neotropical frog.
Carvajal-Castro JD*, Valkonen J, Serrano-Rojas SJ*, Pašukonis A & Rojas B. Does relaxed predation enable rearing-site flexibility in an aposematic poison frog?
Galarza JA, Murphy L, Oudendijk Z, Nissinen R, Burdfield-Steel E, Rojas B, Shulz S, Weiss B, Kaltenpoth M & Mappes J. Beyond pyrazines: microbe-influenced volatile blends contribute to predator aversion in a vertebrate–insect system.
Dittrich C, Jokinen A-K*, Szydlik K, Preininger D, Schweiger S & Rojas B. The warmer, the yellower? Colour patterns of fire salamanders across different temporal scales in the face of climate change.
Carvajal-Castro JD‡*, Rojas-Montoya M‡, Santos JC, Rojas B & Jungwirth A. Large brains are associated with complex habitats, high reproductive investment and long life in Amphibians. (‡Equal contribution).
Rojas-Montaño S*, Rueda LA & Rojas B. Losing the blues: habitat alteration impacts the caudal coloration of the Magdalena river minitegú, Tretioscincus bifasciatus (Sauria: Gymnophthalmidae).
Other publications
(unpublished) Preprints
Sonnleitner R, Alanen E, Fouilloux C, Valkonen J & Rojas B. Genetic factors influence behavioural repeatability in juvenile poison frogs.
Other
6. Hernández-Palma TL, Rueda-Solano LA & Rojas B. 2020. Pleurodema brachyops. Rana de cuatro ojos colombiana. Catálogo de Anfibios y Reptiles de Colombia 6: 27-35. PDF
5. Rojas, B. 2018. Comentario científico: Hacia un estudio integral del papel de los patrones de coloración en las interacciones entre depredadores y presas. Boletín Colombiano de Biología Evolutiva 6: 14-15. PDF
4. Rojas, B. & Burdfield-Steel, E. Predator Defense. 2017. In: J. Vonk & T. K. Shackelford (Eds.). Encyclopaedia of Animal Cognition and Behavior. Springer International Publishing. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-47829-6_708-1 PDF
3. Nokelainen, O., Rojas, B., & Valkonen, J. Camouflage. 2017. In: T. K. Shackelford & V. A. Weekes-Shackelford (Eds.). Encyclopaedia of Evolutionary Psychological Science. Springer International Publishing. DOI:10.1007/978-3-319-16999-6_2665-1 PDF
2. Rojas, B., Nokelainen, O., & Valkonen, J. Aposematism. 2017. In: T. K. Shackelford & V. A. Weekes-Shackelford (Eds.). Encyclopaedia of Evolutionary Psychological Science. Springer International Publishing. DOI:10.1007/978-3-319-16999-6_2669-1 PDF
1. Burdfield-Steel, E. & Rojas, B. 2017. Doubling down. BIOSPHERE Magazine 29:29-36. PDF

